A bright, white smile is often associated with good health and confidence, making teeth whitening one of the most sought-after cosmetic dental procedures today. Whether you’re preparing for a special occasion, aiming to make a positive impression at work, or simply wanting to enhance your overall appearance, teeth whitening can significantly boost your self-esteem. However, understanding the various factors involved in teeth whitening cost can be daunting. From professional treatments to at-home kits, the price of achieving that perfect smile can vary widely. In this blog post, we’ll break down the expenses associated with different teeth whitening options, helping you make an informed decision that suits your budget and needs.
Types of Teeth Whitening Treatments
Teeth whitening treatments come in various forms, each offering different levels of effectiveness and costs. Here’s a detailed look at the main types of teeth whitening treatments available:
1. In-Office Professional Whitening
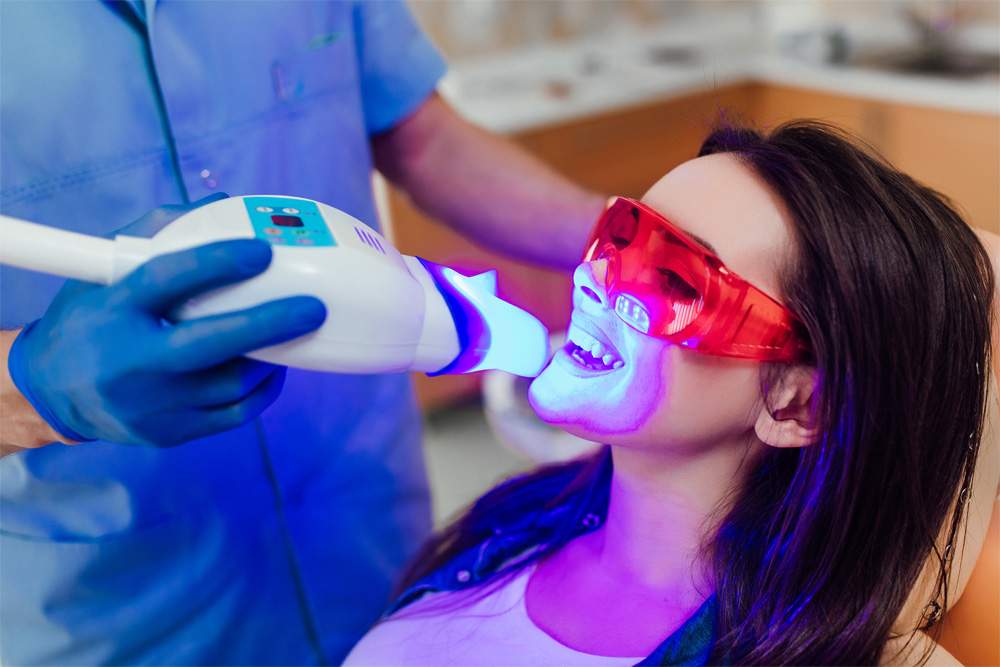
Description and Process: In-office professional teeth whitening is performed by a dentist and involves applying a high-concentration bleaching agent to the teeth. The procedure often includes the use of a special light or laser to enhance the whitening effects.
Average Cost Range: Teeth whitening cost for this treatment typically ranges from Rs.7,000/- to Rs.15,000/- for entire teeth/ sessions.
Factors Influencing Cost:
- Geographic Location: Prices can vary significantly based on the location of the dental office.
- Dentist Expertise: More experienced and reputable dentists may charge higher fees.
- Technology Used: Advanced equipment and techniques can increase the overall cost.
2. At-Home Professional Kits
Description and Process: At-home professional kits are provided by a dentist and include custom-fitted trays and a professional-grade bleaching gel. Patients use these kits at home over a period of time, usually a few weeks.
Average Cost Range: Teeth whitening cost for these kits generally cost around Rs.6,000/- to Rs.12,000/-.
Comparison with In-Office Treatments: While at-home kits are less expensive than in-office treatments, they may take longer to achieve the desired results. However, they still offer a high level of effectiveness compared to over-the-counter products.
3. Over-the-Counter Whitening Products
Types:
- Whitening Strips: Thin, flexible plastic strips coated with a whitening gel.
- Whitening Gels and Pens: Gel applied directly to the teeth with a small brush or pen.
- Whitening Toothpaste and Mouthwash: Products containing mild abrasives and chemical agents to remove surface stains.
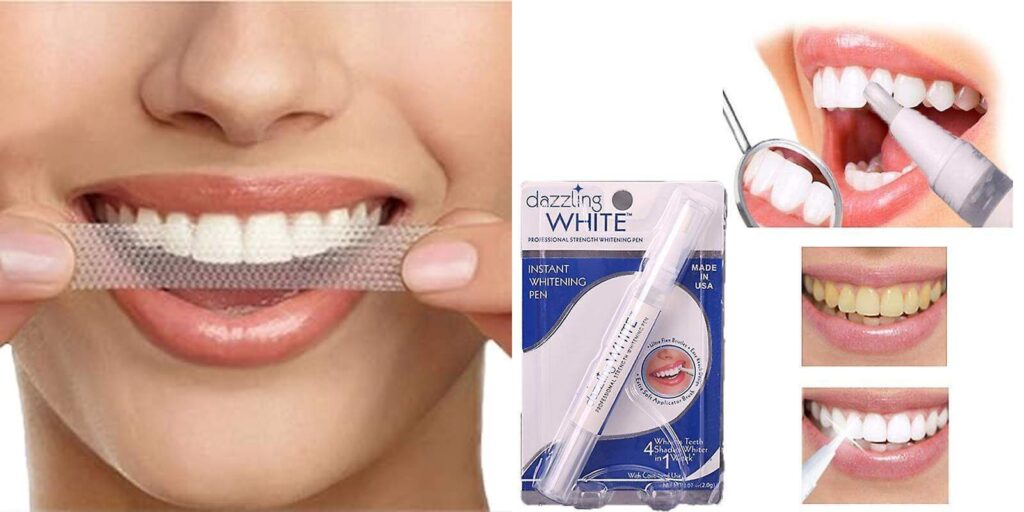

Average Cost Range:
- Whitening Strips: Rs.350 to Rs.1000 per box
- Whitening Gels and Pens: Rs.300 to Rs.800 per product
- Whitening Toothpaste and Mouthwash: Rs.250 to Rs.500 per product
Effectiveness Compared to Professional Treatments: While these products are more affordable, they typically offer less dramatic results and may take longer to see noticeable changes.
4. Natural and DIY Methods
Common Methods:
- Baking Soda: A mild abrasive that can help remove surface stains.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Used in low concentrations as a bleaching agent.
- Oil Pulling: Swishing oil (usually coconut oil) in the mouth to remove stains and improve oral hygiene.
Effectiveness and Safety Concerns: While natural methods can help remove surface stains, they are typically less effective than professional treatments. Additionally, improper use (e.g., using too much baking soda) can damage tooth enamel and gums.
Each of these teeth whitening treatments has its own set of advantages and drawbacks. Your choice will depend on your budget, the level of whitening you desire, and how quickly you want to see results.
Factors Affecting the Teeth Whitening Cost
Teeth whitening cost can vary significantly based on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision and budget accordingly for the treatment that best suits your needs. Here are the main factors that affect the cost of teeth whitening:
1. Geographic Location
Cost Variations by Region: The cost of teeth whitening can differ greatly depending on where you live. Urban areas and regions with a higher cost of living typically have higher prices for dental treatments compared to rural areas. Additionally, international differences can also be significant, with some countries offering more affordable dental services than others.
2. Dentist’s Expertise and Reputation
Impact of Experience and Reputation: Dentists with extensive experience and a strong reputation in cosmetic dentistry often charge higher fees for their services. Their expertise can provide better results and a safer experience, which many patients are willing to pay a premium for.
3. Technology and Equipment Used
Influence of Advanced Technology: The type of technology and equipment used in teeth whitening procedures can also impact the teeth whitening cost. Advanced technologies such as laser or light-activated systems can enhance the effectiveness of the treatment but may come with a higher price tag. Investing in the latest equipment also allows dental practices to offer more efficient and comfortable procedures, justifying the additional cost.
4. Initial Condition of Teeth
Effect of Discoloration Severity: The initial condition of your teeth plays a crucial role in determining the cost of whitening. Teeth that are heavily stained or discolored may require more intensive treatment, longer sessions, or multiple visits, all of which can increase the overall cost. The type of stains (intrinsic vs. extrinsic) can also affect the complexity and price of the procedure.
5. Number of Sessions Required
Single Session vs. Multiple Sessions: Some whitening treatments, especially those done in-office, may achieve desired results in a single session, while others may require multiple visits. Each additional session adds to the total cost, so it’s important to discuss with your dentist how many sessions might be needed to achieve your desired level of whiteness.
6. Post-Treatment Maintenance
Whitening Maintenance Products: To maintain the results of your whitening treatment, you may need to purchase special toothpaste, mouthwash, or touch-up kits. Regular follow-up treatments or maintenance sessions may also be recommended, adding to the long-term cost.
Tips for Reducing Teeth Whitening Costs
Teeth whitening can be expensive, but there are several ways to reduce teeth whitening cost while still achieving a brighter smile. Here are some practical tips to help you save money on teeth whitening treatments:
1. Explore Dental Insurance Options
Check Your Coverage:
- Policy Review: Review your dental insurance policy to see if it covers any part of teeth whitening treatments. While most standard plans do not cover cosmetic procedures, some may offer partial coverage or discounts.
- Supplemental Plans: Consider supplemental dental insurance plans that specifically cover cosmetic procedures, including teeth whitening.
Inquire About Discounts:
- Network Providers: Some insurance plans offer discounts if you choose a dentist within their network.
- Loyalty Programs: Some dental practices have loyalty programs or membership plans that provide discounts on various treatments, including whitening.
2. Look for Discounts and Promotions
Seasonal Offers:
- Holiday Promotions: Many dental offices run special promotions during holidays like Christmas, New Year, or Valentine’s Day, offering discounts on cosmetic procedures.
- Back-to-School Deals: Dental practices sometimes offer back-to-school specials for students and families.
Coupons and Deals:
- Online Platforms: Websites like Groupon and LivingSocial often feature deals on teeth whitening treatments at local dental offices or spas.
- Direct Mail: Keep an eye on your mail for promotional flyers or coupons from local dental offices.
Referral Discounts:
- Refer a Friend: Some dentists offer discounts if you refer new patients to their practice. Ask your dentist if they have a referral program.
3. Consider Financing Options
Payment Plans:
- In-House Financing: Many dental offices offer in-house financing options that allow you to pay for treatments in instalments rather than a lump sum.
- Third-Party Financing: Companies like CareCredit provide healthcare financing options, including for dental procedures, allowing you to spread the cost over several months.
Interest-Free Plans:
- Short-Term Financing: Look for financing plans that offer interest-free periods, making it easier to manage payments without additional costs.
4. Maintain Results to Reduce Re-Treatment Costs
Good Oral Hygiene:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day and flossing daily to prevent stains and plaque buildup.
- Whitening Toothpaste: Use whitening toothpaste to help maintain the results of your whitening treatment.
Dietary Choices:
- Avoid Staining Foods and Drinks: Limit consumption of coffee, tea, red wine, and foods that can stain your teeth. If you do consume them, brush your teeth or rinse your mouth afterward.
- Use a Straw: Drinking beverages through a straw can reduce contact with your teeth, minimizing staining.
Touch-Up Treatments:
- At-Home Maintenance Kits: Invest in professional-grade at-home maintenance kits from your dentist to touch up your whitening as needed, which is more cost-effective than repeated in-office treatments.
- Over-the-Counter Products: Use over-the-counter whitening products for occasional touch-ups to maintain your smile without the high cost of professional treatments.
Regular Dental Check-Ups:
- Preventive Care: Regular dental check-ups and cleanings help maintain your oral health and prolong the results of your whitening treatment. Your dentist can also provide advice on maintaining your white smile.
By exploring these cost-saving strategies, you can achieve and maintain a brighter smile without breaking the bank. Always consult with your dentist to find the most suitable and affordable whitening options for your specific needs.
Conclusion
Teeth whitening can significantly enhance your smile and boost your confidence, but it’s essential to understand the various costs involved to make an informed decision. From professional in-office treatments to at-home kits and natural methods, each option comes with its own set of expenses and effectiveness. By considering factors such as geographic location, dentist expertise, technology used, and maintenance needs, you can better estimate the total cost and choose the best approach for your budget.
Additionally, exploring dental insurance options, looking for discounts and promotions, and considering financing plans can help reduce costs. Maintaining good oral hygiene and making smart dietary choices can also prolong the results, minimizing the need for frequent touch-ups and re-treatments.
Ultimately, investing in teeth whitening is a personal decision that should be based on your specific needs and financial situation. By understanding the breakdown of teeth whitening cost and exploring ways to save, you can achieve a brighter, more radiant smile without straining your budget. Always consult with your dentist to determine the most suitable and cost-effective teeth whitening method for you, ensuring you get the best results for your investment.