As parents, we strive to ensure our children grow up healthy and strong, and a significant part of this journey involves maintaining their dental health. However, navigating the world of pediatric dental care can sometimes be overwhelming, especially when faced with common issues such as cavities, gum disease, and misaligned teeth. These dental problems not only affect a child’s smile but can also impact their overall health and development. Call Dental Xperts to know in depth regarding pediatric dental care and to get answer for all your queries.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for these common pediatric dental issues is crucial for safeguarding your child’s oral health. In this post, we’ll look into the most prevalent dental problems faced by children and provide practical advice on how to prevent them. By taking proactive steps, you can help ensure your child’s teeth remain healthy and strong, paving the way for a lifetime of beautiful smiles. Proper pediatric dental care shall give peace of mind to all parents.
Tooth Decay (Cavities) in Kids
Tooth decay, commonly known as cavities, is one of the most prevalent issue that comes up in pediatric dental care. It occurs when the enamel, the hard outer layer of the teeth, is damaged by acids produced by bacteria. This damage leads to holes or pits in the teeth, which can cause pain and lead to more serious dental problems if left untreated.
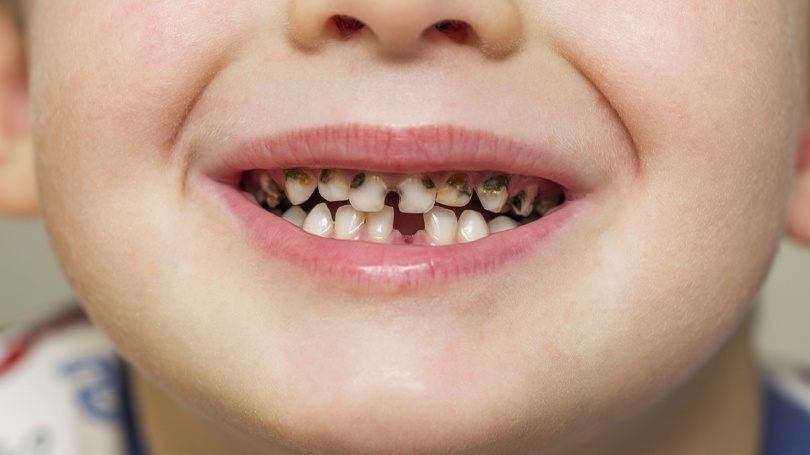
Causes of Tooth Decay
- Bacterial Buildup (Plaque): The primary cause of tooth decay is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When children consume sugary or starchy foods, the bacteria in plaque produce acids that attack the enamel.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can allow plaque to build up, increasing the risk of cavities. Children who do not brush their teeth at least twice a day or floss regularly are more likely to develop tooth decay.
- High Sugar Consumption: Frequent consumption of sugary snacks and drinks, such as candy, soda, and juice, provides fuel for bacteria to produce cavity-causing acids.
Symptoms of Tooth Decay
- Visible Holes or Pits: Cavities often appear as small holes or pits on the surface of the teeth. These may be visible to the naked eye or detected during a dental check-up.
- Tooth Pain or Sensitivity: Children with cavities may experience pain or sensitivity, especially when eating or drinking something sweet, hot, or cold.
- White, Brown, or Black Stains: As decay progresses, it can cause discoloration of the teeth. Early stages may show white spots, while advanced decay may appear as brown or black stains.
Prevention of Tooth Decay
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Teach children to brush their teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and to floss daily. Proper technique is essential to ensure all surfaces of the teeth are cleaned.
- Limiting Sugary Snacks and Drinks: Encourage a balanced diet low in sugary foods and beverages. Substitute sugary snacks with healthier options like fruits and vegetables, and promote drinking water instead of soda or juice.
- Routine Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to the pediatric dentist, starting by the first birthday, can help catch and treat tooth decay early. Dentists can provide professional cleanings and fluoride treatments that strengthen the enamel.
- Fluoride Treatments: Fluoride is a mineral that helps prevent cavities by making the enamel more resistant to acid attacks. Ensure your child uses fluoride toothpaste and ask your dentist about additional fluoride treatments if necessary.
By understanding the causes and symptoms of tooth decay and implementing these preventive measures, parents can help protect their children’s teeth from cavities. Early intervention and consistent dental care are key to maintaining a healthy, cavity-free smile.
Gum Disease (Gingivitis) in Children
Gingivitis, a common and mild form of gum disease, affects the gingiva—the part of the gum around the base of the teeth. While it’s more commonly associated with adults, children can also develop gingivitis. Early detection and proper oral hygiene are crucial to prevent gingivitis from progressing to more serious forms of gum disease.
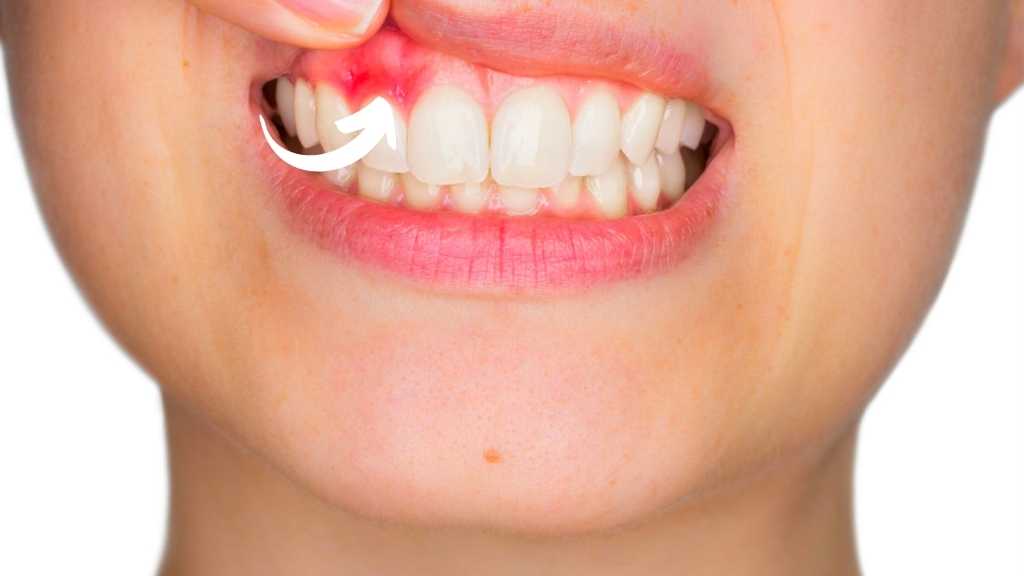
Causes of Gingivitis
- Plaque Buildup: The primary cause of gingivitis is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. When plaque is not removed by brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which further irritates the gums.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque and tartar to accumulate, leading to gum inflammation.
- Diet: A diet high in sugary or starchy foods can contribute to plaque formation. Additionally, a lack of essential nutrients, particularly vitamins C and D, can affect gum health.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes during puberty can increase the sensitivity of the gums, making them more susceptible to gingivitis.
- Mouth Breathing: Breathing through the mouth can cause the gums to dry out, making them more prone to inflammation and infection.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
- Red, Swollen Gums: Healthy gums are typically pale pink. In gingivitis, the gums become red and swollen due to inflammation.
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing are a common sign of gingivitis.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath, or halitosis, can indicate the presence of bacterial infection in the gums.
- Receding Gums: Over time, inflamed gums may begin to recede, making teeth appear longer.
- Tender Gums: Gums may become tender or sore, causing discomfort during eating or brushing.
Prevention of Gingivitis
- Proper Brushing: Encourage your child to brush their teeth twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and teach them to brush gently in circular motions to effectively remove plaque without irritating the gums.
- Regular Flossing: Teach your child to floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gum line where a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Healthy Diet: Provide a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit sugary snacks and drinks, which can contribute to plaque formation.
- Routine Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental visits for professional cleanings and check-ups. A pediatric dentist can remove tartar buildup and monitor your child’s gum health.
- Mouth Rinses: Using an antimicrobial mouth rinse can help reduce plaque and bacteria that cause gingivitis. Consult your dentist for recommendations suitable for children.
When to Seek Professional Help
- Persistent Symptoms: If your child’s gums remain red, swollen, or bleed easily despite good oral hygiene practices, it’s important to consult a dentist.
- Advanced Signs: Symptoms such as receding gums, persistent bad breath, or signs of infection (such as pus between the teeth and gums) require prompt dental evaluation.
- Pain or Discomfort: If your child experiences pain or discomfort in their gums that interferes with eating or brushing, seek professional advice.
Treatment of Gingivitis
- Professional Cleaning: The dentist or dental hygienist will perform a thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums.
- Oral Hygiene Instructions: The dental professional will provide guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques to improve oral hygiene at home.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up visits may be recommended to monitor the condition of the gums and ensure that gingivitis does not progress to more severe gum disease.
Gingivitis is a preventable and treatable condition in pediatric dental care. By promoting good oral hygiene habits and ensuring regular dental visits, parents can help their children maintain healthy gums and prevent the onset of more serious gum diseases. Early intervention is key to reversing gingivitis and maintaining overall oral health.
Malocclusion (Misaligned Teeth) in Children
Malocclusion, commonly known as misaligned teeth, is a condition where the teeth do not fit together correctly when the jaws are closed. This misalignment can affect the bite, speech, and overall oral health. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing malocclusion effectively in children.
Causes of Malocclusion
- Genetic Factors: Malocclusion can be inherited from parents. Children may inherit jaw sizes and shapes that do not align properly, leading to overcrowded or spaced teeth.
- Prolonged Thumb Sucking or Pacifier Use: Persistent thumb sucking or prolonged use of a pacifier beyond the toddler years can exert pressure on the teeth and jaws, leading to misalignment.
- Early Loss of Baby Teeth: Premature loss of baby teeth can cause neighboring teeth to shift into the empty space, disrupting the alignment of incoming permanent teeth.
- Jaw Development Issues: Abnormalities in jaw growth or development can lead to malocclusion. This may include underdeveloped or overdeveloped jaws.
- Dental Habits and Conditions: Other habits, such as tongue thrusting, mouth breathing, and bruxism (teeth grinding), can contribute to malocclusion. Additionally, conditions such as enlarged adenoids or tonsils can affect jaw and teeth alignment.
Symptoms of Malocclusion
- Crooked or Crowded Teeth: Visible misalignment, where teeth appear twisted, overlapping, or too close together.
- Bite Problems: Issues with the way the teeth fit together, including overbite (upper front teeth protrude over the lower teeth), underbite (lower front teeth extend beyond the upper teeth), open bite (front teeth do not meet when the jaws are closed), and crossbite (upper teeth bite inside the lower teeth).
- Difficulty Chewing or Biting: Problems with eating, such as difficulty biting into food or chewing properly.
- Speech Difficulties: Misaligned teeth can affect speech, leading to issues such as lisping or difficulty pronouncing certain sounds.
- Jaw Pain or Discomfort: Misalignment can cause jaw pain, discomfort, or clicking sounds when opening or closing the mouth.
Prevention and Management
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine dental visits are crucial for early detection of malocclusion. Pediatric dentists can monitor the development of a child’s teeth and jaws and identify any alignment issues early on.
- Limit Harmful Habits: Discourage prolonged thumb sucking and pacifier use after age 2-4. Address other habits such as tongue thrusting and mouth breathing that can affect alignment.
- Orthodontic Evaluation: Schedule an orthodontic evaluation around age 7. Orthodontists can assess the development of the teeth and jaws and recommend early interventions if necessary.
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent tooth decay and premature loss of baby teeth, which can contribute to malocclusion.
Treatment of Malocclusion
- Braces: Traditional metal braces are commonly used to correct misaligned teeth. They apply continuous pressure to move teeth into the desired position over time.
- Clear Aligners: Clear aligners, such as Invisalign, are an alternative to braces. They are removable and less noticeable, making them a popular choice for older children and teens.
- Palatal Expanders: For children with narrow upper jaws, a palatal expander can widen the upper jaw to create more space for incoming permanent teeth.
- Retainers: After braces or aligners, retainers are used to maintain the corrected position of the teeth and prevent them from shifting back.
- Tooth Extraction: In cases of severe crowding, the dentist or orthodontist may recommend extracting one or more teeth to create space for proper alignment.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases of jaw misalignment, surgical procedures may be necessary to correct the alignment of the jaws.
Malocclusion is a common dental issue that can have significant impacts on a child’s oral health and overall well-being. Early detection and appropriate treatment are essential to address misaligned teeth and ensure proper pediatric dental care. By working closely with dental professionals, parents can help their children achieve a healthy, well-aligned smile.
Conclusion
Ensuring the dental health of your child is an integral part of their overall well-being. By understanding and recognizing common pediatric dental issues such as tooth decay, early childhood caries, thumb sucking, gum disease, and malocclusion, parents can take proactive steps to ensure better pediatric dental care. Dental clinic in Kakkanad having the best pediatric dentist will assist you all along.
Establishing good oral hygiene habits early on, such as regular brushing and flossing, limiting sugary foods and drinks, and scheduling routine dental check-ups, can significantly reduce the risk of dental issues. Moreover, being vigilant about harmful habits like prolonged thumb sucking or pacifier use, and addressing them promptly, will help maintain proper dental alignment and gum health.
By fostering a positive attitude towards dental care and instilling good habits, you can set your child on a path to a lifetime of optimal oral health. If you have any concerns about your child’s dental health, don’t hesitate to seek advice from your pediatric dentist. They are your best resource for ensuring your child’s teeth and gums remain healthy and strong.