Introduction
Gingivitis, a prevalent form of gum disease, demands attention due to its potential to escalate into more severe oral health issues if left untreated. Fortunately, a range of effective treatments exists to combat this condition and restore gum health. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of gingivitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, various treatment modalities, and essential preventive measures individuals can adopt to maintain robust gum health. With insights from Dental Xperts – Top Dental Clinic in Kakkanad, we aim to provide comprehensive guidance for managing and preventing gingivitis effectively.
Understanding Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common oral health issue characterized by inflammation of the gums. It primarily occurs due to the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth. Plaque forms when bacteria combine with food particles and saliva, accumulating along the gumline and between teeth, which is basically infected gums. Gingivitis is the precursor to gum infection rather than the infection itself. Gingivitis, if left untreated, can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form of gum disease involving gum infection and damage to the surrounding tissues and bone.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
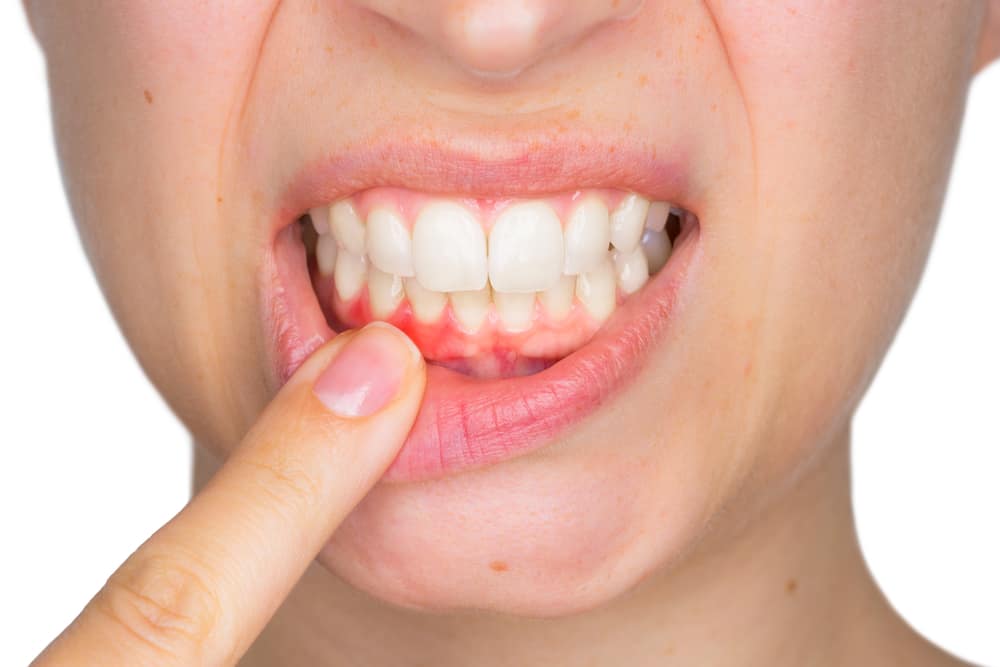
Recognizing the signs of gingivitis is pivotal for timely intervention. Common gum disease symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Formation of pockets between teeth and gums
Prompt consultation with a dentist upon observing these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and formulation of an effective treatment plan.
Gingivitis Treatment Options
Several treatment modalities are available to address gingivitis and restore gum health:
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
Scaling and root planing, a professional dental cleaning procedure, entails the removal of plaque and tartar buildup from teeth and gums, eliminating the source of inflammation. This thorough cleaning is typically performed by a dentist or dental hygienist and may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
2. Enhanced Oral Hygiene Practices
Diligent oral hygiene habits are fundamental in preventing and treating gingivitis. Individuals should brush their teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, ensuring thorough cleaning of all tooth surfaces and along the gumline. Additionally, daily flossing helps remove plaque and debris from between teeth, where toothbrushes cannot reach. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can further reduce bacterial load in the mouth, promoting gum health.
3. Adoption of Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Lifestyle factors such as smoking and poor nutrition can exacerbate gingivitis. Smoking not only weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off gum infections, but it also restricts blood flow to the gums, impairing their ability to heal. Quitting smoking is crucial for improving gum health and enhancing the effectiveness of gingivitis treatment. Moreover, consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support gum health and overall immune function.
4. Antibacterial Therapy
In cases where gingivitis persists despite improved oral hygiene practices, dentists may prescribe antibacterial gingivitis mouth wash or topical gels to help combat bacteria and alleviate inflammation in the gums. These products are typically used as adjuncts to professional dental cleanings and enhanced oral hygiene routines.
5. Regular Dental Check-ups
Routine dental examinations are indispensable for monitoring gum health and detecting gingivitis early. During dental check-ups, dentists assess the condition of the gums, teeth, and surrounding oral tissues, identifying any signs of inflammation or infection. Early detection enables timely intervention, preventing gingivitis from progressing to more severe forms of periodontal disease.
Prevent Gingivitis
Prevention remains paramount in mitigating the risk of gingivitis. Key preventive measures include:
1. Sustaining Optimal Oral Hygiene
Consistent brushing and flossing to remove plaque and prevent bacterial buildup are essential preventive measures against gingivitis. Individuals should brush their teeth thoroughly for at least two minutes twice daily, paying special attention to the gumline and chewing surfaces. Flossing should be done once a day to remove plaque from between teeth and along the gumline, where toothbrushes cannot reach.
2. Scheduled Dental Visits
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are imperative for monitoring oral health status and addressing any emerging issues promptly. Dentists recommend scheduling dental visits every six months for most individuals, although the frequency may vary based on individual risk factors and oral health needs. During dental appointments, dentists not only clean teeth and remove plaque and tartar but also assess gum health and provide personalized recommendations for maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
3. Tobacco Cessation
Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of gingivitis and other oral health problems. Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off gum infections. It also restricts blood flow to the gums, impairing their ability to heal and increasing the likelihood of gum disease. Individuals who smoke should consider seeking support from healthcare professionals or smoking cessation programs to quit successfully.
4. Nutritious Dietary Choices
A balanced diet comprising essential vitamins and minerals fosters gum health and augments overall oral hygiene. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, promote gum tissue healing and support immune function. Calcium-rich foods like dairy products and leafy green vegetables help strengthen tooth enamel and maintain bone density, reducing the risk of gum disease. Additionally, drinking plenty of water helps rinse away food particles and bacteria from the mouth, reducing plaque accumulation and lowering the risk of gingivitis.
5. Stress Management
Stress compromises the immune system, predisposing individuals to gum disease. Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation in the body, including the gums, making individuals more susceptible to gingivitis and other oral health problems. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga into daily routines, which are the most natural gingivitis treatment methods, can help individuals manage stress more effectively, promoting overall well-being, including gum health.
Gingivitis treatment at home and how long to heal
The duration for healing and curing gum disease at home can typically range from a few months to upwards of six months or more, depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the chosen treatments. However, more advanced stages of gum disease, such as moderate to severe periodontitis, may require several months of dedicated treatment, including professional interventions like deep cleaning procedures and ongoing monitoring by a dentist or periodontist. It’s essential to maintain patience and persistence in following recommended home care routines and to seek professional guidance if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Conclusion
Gingivitis, though common, warrants proactive management to forestall its progression to more severe oral health complications. By grasping the nuances of gingivitis, individuals can arm themselves with knowledge to identify symptoms, pursue appropriate gingivitis treatment avenues, and adopt preventive measures to safeguard gum health. With guidance from Dental Xperts having the top dentists in Kochi, prioritizing good oral hygiene, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and embracing a healthy lifestyle are cornerstones of effective gingivitis management and prevention. Through these concerted efforts, individuals can maintain optimal gum health and enjoy a lifetime of healthy smiles.